One of the refrigerant you can find in most modern cooling systems is R-448A. The refrigerant, which falls under the category of HFOs, is a zeotropic blend that consists of 2 HFOs (R1234ze and R1234yf) and 3 HFC refrigerants (R134A, R125, and R32).
The refrigerant (also known as Solstice N40) is a product of Honeywell and has become as a suitable alternative replacement for R-404A, R-134A, R-507, and R-22 refrigerants.
If you are a technician that wants in-depth information about the refrigerant, this article is for you. We’ll provide a detailed fact sheet of R448A, a PT chart, its benefits, limitations, and compare it to other refrigerants such as R404A.
Let’s get started!
What is R-448A Refrigerant?
The R-448A refrigerant (product name: Solstice N40) is a refrigerant that falls under the category of Hydrofluroolefin (HFOs). It’s a refrigerant blend consisting of 5 HFC and 2 HFO components. They include:
| Refrigerant | Type of Refrigerant | % in the refrigerant |
| R1234ZE | HFO | 7% |
| R1234YF | HFO | 20% |
| R-134A | HFC | 21% |
| R-125 | HFC | 26% |
| R-32 | HFC | 26% |
Why Was R-448A created
In recent years, governing bodies such as the European Union (EU) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have been working on eliminating refrigerants that destroy the environment. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFC) were the first refrigerants to be phased out because they depleted the ozone layer.
Hydrofluorocarbons came in as the third generation, and they too, are in the process of being phased out because of their high global warming potential.
As a result, companies (such as Honeywell and Chemours) started coming up with the fourth generation of refrigerants, hydrofluroolefin (HFOs).
R448A was one of the products created by Honeywell. They created the refrigerant to replace R-404A, which is an HFC refrigerant with a high global warming potential (GWP) of almost 4000.
Why is R-448A a good replacement for R-404A
R-448A has a lower GWP (around 1300) which makes it a suitable replacement in systems that use R-404A.
Honeywell also says that replacing R-404A refrigerants with R-448A presents two significant benefits.
- 5-15% drop in energy consumption: In addition to a 70% GWP, using R-448A means that systems that use the HFO refrigerant will no longer consume a lot of power during cooling
- Increased cooling capacity: Since using R-448A will save on energy costs, this makes the system that uses this refrigerant efficient at cooling, especially in larger units.
Other refrigerants that R-448A will replace:
In our investigations, we also discovered that R-448A would also replace two other refrigerants:
- R-22: a HCFC, known to have a high ozone depleting potential
- R-134A: A HFC, commonly used in transport refrigeration and automotive air conditioning systems
- R-507A: Another HFC, commonly used in insulated transport, commercial refrigeration, and industrial refrigeration. The refrigerant has a GWP close to 4000, which is almost four times higher than that of R-448A
A Detailed R448A Fact Sheet
For more information on R-448A, here’s a detailed fact sheet for the refrigerant. If you need more information about it, contact us.
| Name: | R448A |
|---|---|
| Name (2): | Solstice N40 |
| Classification: | Hydrofluoroolefin |
| Chemistry: | R1234ze//R1234yf/R134a/R125/R32 |
| Status: | Active & Growing |
| Future: | Will be phased out from 2024 |
| System Type: | Low and medium temperature refrigeration systems |
| Application: | ice-cream and ice-making machines, refrigerated display cases, refrigerated counters |
| Application (2): | Commercial Refrigeration: Plug-Ins & Vending Machines |
| Application (3): | Industrial Refrigeration |
| Application (4): | cold storage rooms |
| Replacement For: | R-404A, R-134A, R-507, R-22 |
| Ozone Depletion Potential: | 0 |
| Global Warming Potential: | Appro. 1300 |
| Global Warming Risk: | Moderately high |
| Toxicity Levels: | Low degree toxicity (A1) |
| Flammability Levels: | Class 1 - No Flame Propagation |
| Lubricant Required: | POE |
| Boiling Point: | -45.9 °C ( -43.27 °F) |
| Critical Temperature: | 83.7 ℃ (182.6 °F) |
| Critical Pressure: | 46.6 bar (675.9 psi) |
| Temperature Glide: | 6.25K |
| Molar Mass: | 86.3 g·mol−1 |
| Critical Density | 480.2 kg/m3 |
| Melting Point: | Unknown |
| Vapor Pressure: | 11.24 bar (25 °C) |
| Manufacturers: | Honeywell |
| Manufacturing Facilities: | All Over Including: USA, Mexico, EU, China, and others. |
| Form: | Gas |
| Color: | Unknown |
| Odor | slight ether-like odor as a liquified gas |
| EPA Certification Required: | 608 or 609 Required |
| Require Certification to Purchase? | Yes |
| Cylinder Color: | Unknown |
| Purchasing: | Buy R448A in Bulk |
R-448A Pressure Temperature Chart
When providing a refrigerant’s fact & info sheet, we always like to provide the pressure-temperature chart for the refrigerant. Technicians need this information during inspection, repairs, or replacements.
A pressure-temperature chart is essential in helping the expert know the exact pressure the refrigerant will be at a specific temperature. The chart also provides the subcool, superheat, and the saturation points of the refrigerant. The technicians doesn’t need to do any trial and error during charging or replacement because doing so can damage the refrigeration components or the entire unit.
Here’s a comprehensive R448A PT chart we created.
| PSIG | Liquid Temp (F) | Liquid Temp (C) | Vapor Temp (F) | Vapor Temp (C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -51 | -46.11 | -39.9 | -39.94 |
| 1 | -48.6 | -44.78 | -37.5 | -38.61 |
| 2 | -46.2 | -43.44 | -35.2 | -37.33 |
| 3 | -44 | -42.22 | -32.9 | -36.06 |
| 4 | -41.9 | -41.06 | -30.8 | -34.89 |
| 5 | -39.8 | -39.89 | -28.8 | -33.78 |
| 6 | -37.8 | -38.78 | -26.9 | -32.72 |
| 7 | -35.9 | -37.72 | -25 | -31.67 |
| 8 | -34.1 | -36.72 | -23.2 | -30.67 |
| 9 | -32.4 | -35.78 | -21.4 | -29.67 |
| 10 | -30.6 | -34.78 | -19.7 | -28.72 |
| 11 | -29 | -33.89 | -18.1 | -27.83 |
| 12 | -27.4 | -33 | -16.5 | -26.94 |
| 13 | -25.8 | -32.11 | -15 | -26.11 |
| 14 | -24.3 | -31.28 | -13.5 | -25.28 |
| 16 | -21.4 | -29.67 | -10.6 | -23.67 |
| 18 | -18.6 | -28.11 | -7.8 | -22.11 |
| 20 | -16 | -26.67 | -5.2 | -20.67 |
| 22 | -13.5 | -25.28 | -2.7 | -19.28 |
| 24 | -11 | -23.89 | -0.3 | -17.94 |
| 26 | -8.7 | -22.61 | 2 | -16.67 |
| 28 | -6.5 | -21.39 | 4.2 | -15.44 |
| 29 | -5.4 | -20.78 | 5.3 | -14.83 |
| 31 | -3.3 | -19.61 | 7.4 | -13.67 |
| 34 | -0.2 | -17.89 | 10.4 | -12 |
| 37 | 2.7 | -16.28 | 13.3 | -10.39 |
| 40 | 5.5 | -14.72 | 16 | -8.89 |
| 43 | 8.2 | -13.22 | 18.7 | -7.39 |
| 46 | 10.8 | -11.78 | 21.2 | -6 |
| 49 | 13.2 | -10.44 | 23.7 | -4.61 |
| 52 | 15.6 | -9.11 | 26 | -3.33 |
| 55 | 17.9 | -7.83 | 28.3 | -2.06 |
| 59 | 20.9 | -6.17 | 31.2 | -0.44 |
| 63 | 23.8 | -4.56 | 34 | 1.11 |
| 67 | 26.5 | -3.06 | 36.7 | 2.61 |
| 83 | 36.5 | 2.5 | 46.6 | 8.11 |
| 101 | 46.5 | 8.06 | 56.3 | 13.5 |
| 121 | 56.2 | 13.44 | 65.9 | 18.83 |
| 142 | 65.4 | 18.56 | 74.9 | 23.83 |
| 154 | 70.2 | 21.22 | 79.6 | 26.44 |
| 167 | 75.1 | 23.94 | 84.4 | 29.11 |
| 181 | 80.2 | 26.78 | 89.3 | 31.83 |
| 196 | 85.3 | 29.61 | 94.3 | 34.61 |
| 212 | 90.5 | 32.5 | 99.3 | 37.39 |
| 229 | 95.7 | 35.39 | 104.3 | 40.17 |
| 246 | 100.7 | 38.17 | 109.1 | 42.83 |
| 264 | 105.6 | 40.89 | 113.9 | 45.5 |
| 284 | 110.9 | 43.83 | 119 | 48.33 |
| 304 | 115.9 | 46.61 | 123.8 | 51 |
| 325 | 121 | 49.44 | 128.6 | 53.67 |
| 348 | 126.2 | 52.33 | 133.6 | 56.44 |
| 349 | 126.4 | 52.44 | 133.8 | 56.56 |
| 372 | 131.4 | 55.22 | 138.5 | 59.17 |
| 397 | 136.6 | 58.11 | 143.4 | 61.89 |
| 423 | 141.8 | 61 | 148.3 | 64.61 |
| 450 | 146.9 | 63.83 | 153 | 67.22 |
R448A Applications
R448A is useful in various low to medium refrigeration applications. These include:
- Cold storage rooms
- Water refrigerators
- Ice-cream making machines
- Transport refrigeration
Pros of Y R-448a Refrigerant
Now that you know what R-448A is all about, what are some of the benefits you can expect to get when using this refrigerant? Let’s find out.
1. It has a lower GWP
Considering the fact that R448A has a lower GWP of around 1300 – a value four times lesser than the refrigerant it replaces (R404A), it makes it a suitable refrigerant to use. Of course, there are other refrigerants that have a lower value than it; however, it’s better to use a cooling fluid that has lesser impact on the environment in case of a leakage.
2. It has low toxicity and flammability
When ASHRAE (American Society of Heating and Air Conditioning Engineers) are considering the safety of a refrigerant, they consider two things. One is the level of toxicity within the refrigerant, and two, it’s the flammability levels in case it gets into contact with fire.
R-448A has Class A classification. Which means there’s no toxicity at concentrations less than or equal to four-hundred parts per million. It also has a Class 1 flammability classification. In case of a fire or accident, the gas will not explode.
If you want to learn more about refrigerant toxicity and flammability, read more on this article.
3. It has better thermodynamic properties to R404A
Normally, refrigerants have three properties: Chemical, thermodynamic, and physical properties. Technicians will consider four major things when examining the thermodynamic properties of a refrigerant. This includes the volume, pressure, temperature, and entropy. You can refer to the table above to confirm the properties of R448A.
In a study done to compare the thermodynamic properties of R-404A and R-448A, scientists found that R-448A had better heat transfer coefficients than R-404A. Therefore, this makes R-448A one of the most energy efficient replacements for r404A because systems do not have to use a lot of power to cool a system or a unit.
Limitations/Problems of the Refrigerant
Although R-448A is an energy-efficient, it doesn’t come without a few challenges or limitations. One obvious challenge is the GWP.
For instance, R-1234yf – which is an HFO refrigerant within this blend, has a GWP value of 4. Hence, it can be toxic to the environment when used in large quantities. It’s one of the refrigerants that will be phased out under the F-gas Regulation because of its high GWP.
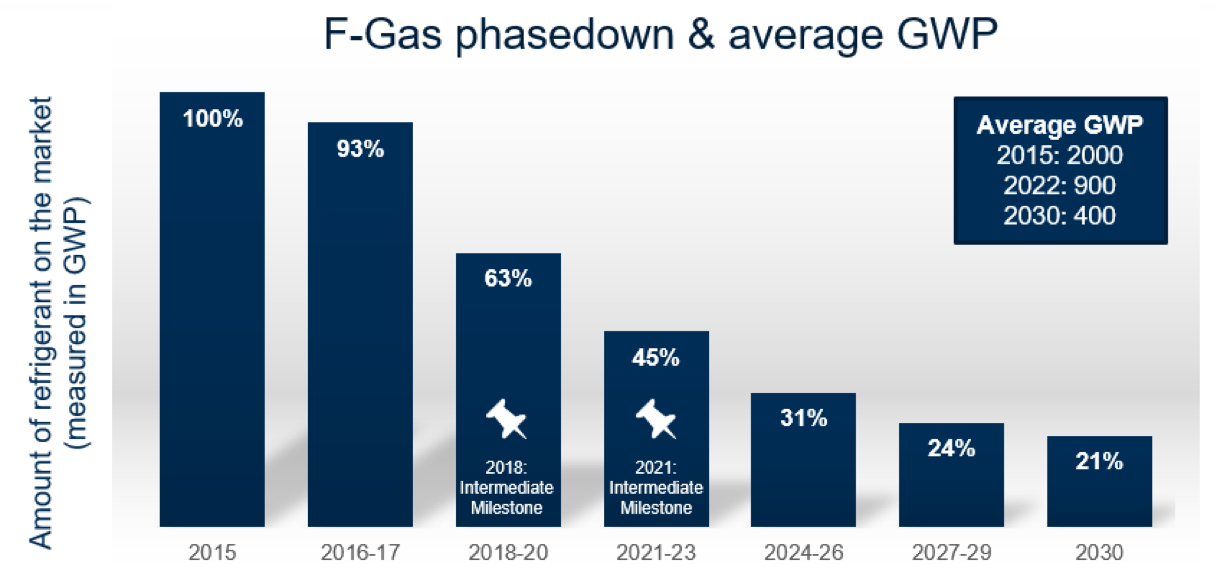
The other problem that you should be keen to note is that R-448A is not a retrofit replacement of R404A systems. According to a retrofitting guide for R-448A provided by Honeywell, you’ll need to check the system components to see if it’s compatible with R-448A. For instance, you might need to change the lubricant if it’s not compatible with R-448A.
Otherwise, you can end up damaging the entire unit if you don’t change certain components. This also means that the replacement costs will increase since you’ll have to purchase replacements to fit R448A into a R404A system.
Conclusion
We have come to the end of the article, folks. That’s all you need to know about the refrigerant, R-448A. Note that, although it’s an efficient fluid for various cooling applications, we may never use it for long because of its high GWP value.